How Microsoft’s AI Security Agents Work
Microsoft has introduced Security Copilot AI agents to help security teams handle cyber threats faster. These agents use AI to analyze phishing attacks, detect vulnerabilities, and prioritize alerts. Instead of relying only on human security teams, organizations can now use AI-driven tools to automate responses and reduce workload. The shift toward AI-powered security aims to help businesses stay ahead of cyber threats that are increasing in complexity and volume.
Security teams often struggle with the sheer number of threats they face daily. With thousands of cyberattacks occurring every second, manual analysis can’t keep up. AI security agents are designed to automate repetitive tasks, allowing security professionals to focus on high-risk incidents rather than getting bogged down by false positives and routine monitoring.
What Makes Microsoft Security Copilot Different?
Unlike standard security tools, Security Copilot agents work autonomously. They process massive amounts of security data, detect potential threats, and provide recommendations. Microsoft has developed six AI agents for different security tasks:
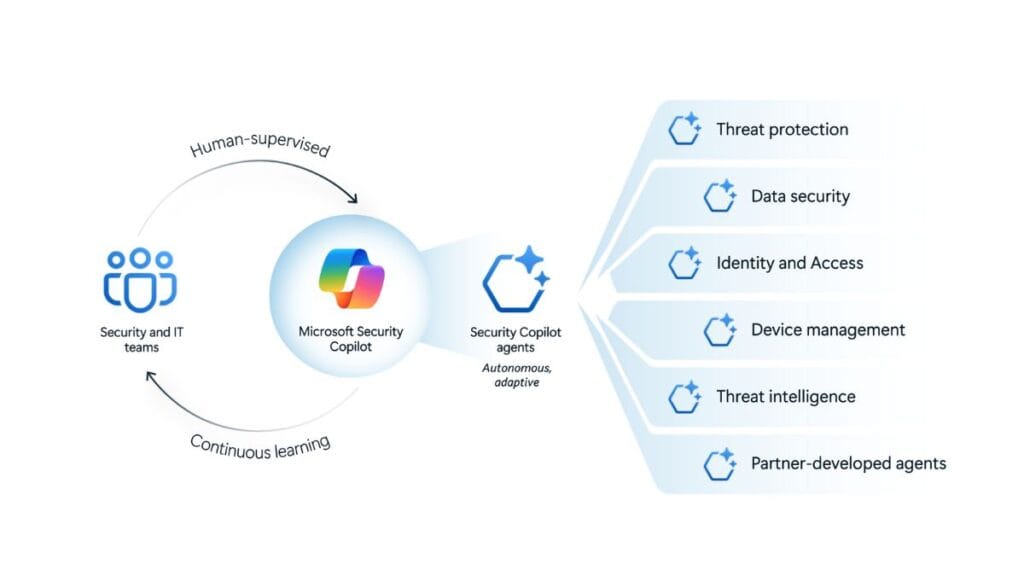
- Phishing Triage Agent: Identifies phishing attempts and reduces false alerts, improving efficiency for security teams.
- Alert Triage Agents: Sort through security alerts to highlight critical risks and minimize response time.
- Conditional Access Optimization Agent: Detects access policy gaps and suggests fixes, improving identity security.
- Vulnerability Remediation Agent: Monitors and prioritizes software vulnerabilities, helping organizations reduce potential attack surfaces.
- Threat Intelligence Briefing Agent: Generates security threat reports, providing real-time analysis of emerging cyber threats.
- Data Security Investigation Agent: Helps organizations manage data breaches by analyzing incidents and recommending actions.
These AI tools integrate with Microsoft Defender, Entra, and Intune, giving security teams a centralized AI-powered defense system. By automating routine security tasks, organizations can improve their ability to detect, analyze, and respond to threats faster.
Does the Hype Match Reality?
Microsoft presents these AI agents as game-changing security tools, but real-world challenges remain. Here are some key concerns:
False Positives Can Overload Security Teams
AI-driven security tools aren’t perfect. If an agent incorrectly flags safe emails as phishing, security teams may waste time reviewing false alerts. The same issue applies to vulnerability detection—misclassifications could lead to unnecessary software updates or missed threats. When security teams become overwhelmed with false alerts, they might miss critical attacks that slip through the cracks.
Security professionals often emphasize the need for a balanced approach, where AI handles low-level threats while humans manage high-risk cases. Without this balance, AI security agents may become a burden rather than a solution.
Security Blind Spots and AI Limitations
AI models are trained on past data, which means they might not catch new or highly sophisticated cyberattacks. Hackers continually evolve their tactics, and AI tools may struggle to identify novel threats without human oversight. Attackers can also manipulate AI models by feeding them misleading data, potentially reducing their effectiveness.
Another issue is data dependency—AI security agents rely on Microsoft’s datasets, which may not always reflect the unique threat landscape of individual businesses. Companies must consider how well these AI tools align with their specific security challenges.
Dependence on Microsoft’s Ecosystem
Security Copilot is designed for businesses that already use Microsoft security tools. If a company uses non-Microsoft security software, integration could be difficult or require additional investment in Microsoft’s ecosystem. This can create vendor lock-in, making it harder for companies to switch providers or use alternative security solutions that may better fit their needs.
Adoption Challenges for Businesses
Despite its potential, organizations face several barriers when considering AI-driven security solutions:
Cost and Budget Concerns
While AI security tools can improve efficiency, they come at a price. Many companies, especially small businesses, may find it too expensive to implement Microsoft’s full security suite. Subscription-based pricing models and licensing fees can add up, making it harder for organizations with limited budgets to justify the investment.
Additionally, AI-driven security tools require ongoing updates and maintenance, which may involve extra costs for training staff, adjusting workflows, and integrating new security measures.
IT Team Resistance and Learning Curve
Security teams that already have established processes might be hesitant to rely on AI for threat detection. Some IT professionals prefer manual analysis, fearing that automation could reduce control over security decisions. The transition to AI-powered security requires new skills, and teams may need time to adapt to the new workflows.
A key challenge is trust—security teams must have confidence that AI agents are making the right decisions. If AI-generated alerts lack transparency or provide unclear explanations, professionals may resist using them, limiting their effectiveness.
Compatibility with Existing Security Systems
Many organizations use multiple security vendors. If Microsoft’s AI agents don’t integrate smoothly with third-party security tools, businesses may hesitate to switch. Security teams often rely on a mix of on-premise and cloud-based solutions, and any incompatibility could disrupt existing operations.
How Microsoft Compares to Other AI Security Tools
Microsoft isn’t the only company introducing AI-driven security solutions. Google and Amazon are also developing AI tools to handle cybersecurity threats. Here’s how Microsoft compares:
- Google Security Operations: Uses AI to analyze security logs but lacks built-in AI agents for automated response.
- Amazon GuardDuty: Detects AWS security threats but focuses primarily on cloud security, unlike Microsoft’s broader approach.
- CrowdStrike Falcon: Offers behavior-based threat detection, but doesn’t automate responses like Security Copilot.
While Microsoft’s AI agents provide strong automation, businesses need to evaluate whether they fit their security needs and infrastructure. Some organizations may prefer security solutions that offer more flexibility and integration options beyond the Microsoft ecosystem.
What This Means for Businesses
Microsoft’s Security Copilot AI agents have the potential to redefine how security teams operate. However, businesses must weigh the benefits against the risks. While AI automation can save time and improve threat detection, companies should ensure they maintain human oversight and verify AI-generated alerts.
For businesses considering AI security tools, the key questions are:
- Does AI security fit within your existing security strategy?
- How much human intervention is still required?
- Will AI tools improve efficiency without creating new risks?
Security AI is still evolving, and organizations must decide whether they are ready to trust AI agents with critical cybersecurity decisions or if human expertise remains essential in high-risk scenarios. The future of cybersecurity will likely involve a hybrid approach, where AI handles routine tasks while human analysts focus on strategic threats.